Item discrimination parameters are generally unwanted and inestimable in a Rasch measurement context. The two-parameter logistic model (2-PL) and its rating-scale brothers (Muraki, 1997) include item discrimination parameters, ai:

The failure of such models to be Rasch models is seen from their lack of construct stability - the item hierarchy changes with person performance level. The condition that the estimate of ai must satisfy is
![]()
It is seen that the other parameters interact with the data {xni} on the left side of this equation. This implies that the family of 2-PL models lacks the parameter separability and objectivity necessary for measurement construction.
There are, however, Rasch models that do support discrimination parameters. Two examples are the Poisson Count and Binomial Trials models. The utility of these discrimination parameters is that they allow the construction of a more coherent measurement system when Poisson count and binomial trial items are included in tests containing items with varying formats.
The Poisson Count model is used for counting conceptually rare independent events, such as spelling mistakes in a dictation test or home runs by a baseball team. The basic model is:
![]()
The expression loge(x) represents the pre-determined structure of the infinitely long rating scale. This fixed structure allows the application of a discrimination parameter to the rating scale, but not to the other parameters:
![]()
This is a Rasch model because ai does not perturb the item hierarchy {Di}. ai must satisfy:
![]()
It is seen that the left side of this equation is free of the other parameters. Parameter separability has been obtained.
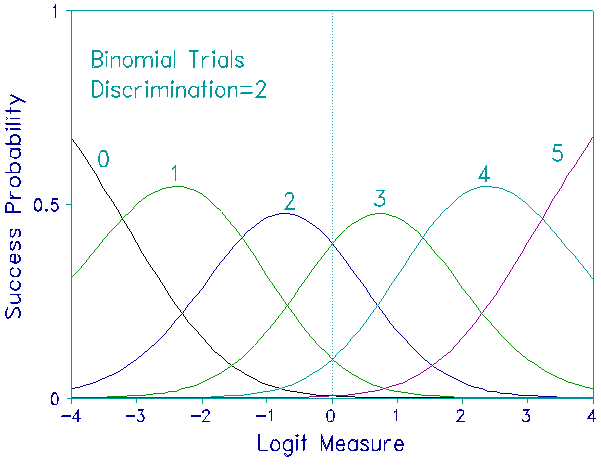
Similarly a discrimination parameter can be added to the Binomial Trials model, used to count the number of successes, x, in m attempts:
![]()
In the Rasch "Inverse Binomial (or MASI) Model" (Spray, 1997), used to count the number of attempts, x, until m successes have been obtained, a discrimination parameter ai can also be included:
![]()
This is also true of the mirror image of that model used to count the number of attempts, x, until m failures have been obtained:
![]()
John Michael Linacre
Muraki E. 1997. A generalized partial credit model. Chapter 9 in W. van der Linden & RK Hambleton (Eds.) Handbook of Modern Item Response Theory. New York: Springer.
Spray JA. 1997. Multiple attempt, single item response models. Chapter 12 in ibid.